When Code Begins to Dream: Anthropomorphism in AI Powered Educational Tools
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14456/jcct.2025.25คำสำคัญ:
Anthropomorphism, Artificial Intelligence, Educational Tools, Ethics, Studentsบทคัดย่อ
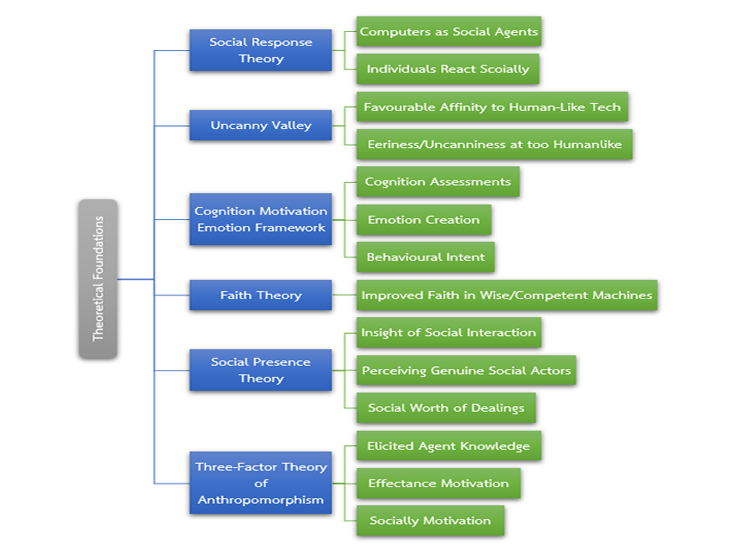
Anthropomorphism, the attribution of human traits to non-human creatures, has become popular in artificial intelligence-powered educational technologies to improve user interaction and learner engagement. This study examines the importance of anthropomorphism in AI-driven educational aids, analysing its psychological foundations, use in large language models (LLMs), and effects on student learning outcomes. This paper employs a conceptual analysis of current AI products (e.g., ChatGPT, DuoLingo Max) and utilises theoretical frameworks such as Social Presence Theory and the Uncanny Valley hypothesis to investigate the impact of human-like design elements—voice, emotion, and behaviour—on learner motivation, trust, and comprehension. The discourse encompasses advantages, such as enhanced engagement and tailored feedback, as well as concerns, including emotional manipulation, misrepresentation of AI capabilities, and diminished critical thinking. The study concludes that although anthropomorphism can greatly improve educational experiences, its implementation must be meticulously adjusted to prevent ethical dilemmas and reliance.
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Adam, M., Wessel, M., & Benlian, A. (2021). AI-based Chatbots in Customer Service and Their Effects on User Compliance. Electronic Markets, 31(2), 427-445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12525-020-00414-7.
Airenti, G. (2015). The Cognitive Bases of Anthropomorphism: From Relatedness to Empathy. International Journal of Social Robotics, 7(1), 117-127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12369-014-0263-x.
Angelov, P. P., & Gu, X. (2018). Toward Anthropomorphic Machine Learning. Computer, 51(9), 18-27. https://doi.org/10.1109/MC.2018.3620973.
Araujo, T. (2018). Living Up to the Chatbot Hype: The Influence of Anthropomorphic Design Cues and Communicative Agency Framing on Conversational Agent and Company Perceptions. Computers in Human Behavior, 85, 183-189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.03.051.
Babu, C. V. S., & Adhithya, S. (2023). ChatGPT and Other Generative AI Tools in Education: Transformative Potential and Ethical Considerations. In Keengwe, J. (Eds), Advances in Educational Technologies and Instructional Design (135-152). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/979-8-3693-0205-7.ch007.
Bai, J., Bai, S., Yang, S., Wang, S., Tan, S., Wang, P., Lin, J., Zhou, C., & Zhou, J. (2023). Qwen-VL: A Versatile Vision-Language Model for Understanding, Localization, Text Reading, and Beyond. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2308.12966.
Basyal, L., & Sanghvi, M. (2023). Text Summarization Using Large Language Models: A Comparative Study of MPT-7b-instruct, Falcon-7b-instruct, and OpenAI Chat-GPT Models. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2310.10449.
Buscemi, A., & Proverbio, D. (2024). ChatGPT vs Gemini vs LLaMA on Multilingual Sentiment Analysis. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2402.01715.
Cao, C., Zhao, L., & Hu, Y. (2019, July 8-12). Anthropomorphism of Intelligent Personal Assistants (IPAs): Antecedents and Consequences. Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems 2019, 187. X'ian, China.
Choi, S., Liu, S. Q., & Mattila, A. S. (2019). “How May I Help You?” Says a Robot: Examining Language Styles in the Service Encounter. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 82, 32-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2019.03.026.
Deshpande, A., Rajpurohit, T., Narasimhan, K., & Kalyan, A. (2023). Anthropomorphization of AI: Opportunities and Risks. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2305.14784.
Devlin, J., Chang, M. -W., Lee, K., & Toutanova, K. (2018). BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.1810.04805.
Dhagare, R. P. (2024). Generative AI and Education: A Symbiotic Relationship. International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology, 12(11), 1042-1045. https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.65279.
Diederich, S., Lichtenberg, S., Brendel, A. B., & Trang, S. (2019, December 15-18). Promoting Sustainable Mobility Beliefs with Persuasive and Anthropomorphic Design: Insights from an Experiment with a Conversational Agent. International Conference on Information Systems 2019, 1-17. Munich, Germany.
Epley, N., Waytz, A., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2007). On Seeing Human: A Three-Factor Theory of Anthropomorphism. Psychological Review, 114(4), 864-886. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.114.4.864.
Epley, N., Waytz, A., Akalis, S., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2008). When We Need a Human: Motivational Determinants of Anthropomorphism. Social Cognition, 26(2), 143-155. https://doi.org/10.1521/soco.2008.26.2.143.
Gómez Cano, C. A., & Colala Troya, A. L. (2023). Artificial Intelligence Applied to Teaching and Learning Processes. LatIA, 1, 2. https://doi.org/10.62486/latia20232.
Gursoy, D., Chi, O. H., Lu, L., & Nunkoo, R. (2019). Consumers Acceptance of Artificially Intelligent (AI) Device Use in Service Delivery. International Journal of Information Management, 49, 157-169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.03.008.
Hou, G., & Lian, Q. (2024). Benchmarkin0067 of Commercial Large Language Models: ChatGPT, Mistral, and Llama. Research Square. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-4376810/v1.
Igbokwe, I. C. (2023). Application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Educational Management. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 13(3), 300-307. https://doi.org/10.29322/IJSRP.13.03.2023.p13536.
Kim, S. Y., Schmitt, B. H., & Thalmann, N. M. (2019). Eliza in the Uncanny Valley: Anthropomorphizing Consumer Robots Increases Their Perceived Warmth but Decreases Liking. Marketing Letters, 30(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11002-019-09485-9.
Lee, J. -G., Kim, K. J., Lee, S., & Shin, D. -H. (2015). Can Autonomous Vehicles Be Safe and Trustworthy? Effects of Appearance and Autonomy of Unmanned Driving Systems. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 31(10), 682-691. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2015.1070547.
Liu, Y., Iter, D., Xu, Y., Wang, S., Xu, R., & Zhu, C. (2023, December 6 –10). G-Eval: NLG Evaluation using GPT-4 with Better Human Alignment. The 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2511-2522. Association for Computational Linguistics, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2023.emnlp-main.153.
Moussawi, S., Koufaris, M., & Benbunan-Fich, R. (2021). How Perceptions of Intelligence and Anthropomorphism Affect Adoption of Personal Intelligent Agents. Electronic Markets, 31(2), 343-364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12525-020-00411-w.
Niu, D., Terken, J., & Eggen, B. (2018). Anthropomorphizing Information to Enhance Trust in Autonomous Vehicles. Human Factors and Ergonomics in Manufacturing & Service Industries, 28(6), 352-359. https://doi.org/10.1002/hfm.20745.
Nowak, K. L., & Biocca, F. (2003). The Effect of the Agency and Anthropomorphism on Users’ Sense of Telepresence, Copresence, and Social Presence in Virtual Environments. Presence: Teleoperators and Virtual Environments, 12(5), 481-494. https://doi.org/10.1162/105474603322761289.
Raffel, C., Shazeer, N., Roberts, A., Lee, K., Narang, S., Matena, M., Zhou, Y., Li, W., & Liu, P. J. (2020). Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 21(140), 1-67.
Reddy, A., Nicenboim, I., Pierce, J., & Giaccardi, E. (2021). Encountering Ethics through Design: a Workshop with Nonhuman Participants. AI & Society, 36(3), 853–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-020-01088-7.
Ren, M. (2024). Advancements and Applications of Large Language Models in Natural Language Processing: A Comprehensive Review. Applied and Computational Engineering, 97(1), 55-63. https://doi.org/10.54254/2755-2721/97/20241406.
Schroeder, J., & Schroeder, M. (2018, January 3- 6). Trusting in Machines: How Mode of Interaction Affects Willingness to Share Personal Information with Machines. The 51st Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences 2018, 472-480. Hawaii, United States of America. https://doi.org/10.24251/hicss.2018.061.
Scorici, G., Schultz, M. D., & Seele, P. (2024). Anthropomorphization and Beyond: Conceptualizing Humanwashing of AI-Enabled Machines. AI & Society, 39(2), 789-795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-022-01492-1.
Shaikhiyeva, Z., Mansurova, M., & Amirkhanova, G. (2024, October 26-28). Text to SQL Transformation Using LLM: A Comparative Research of T5, Seq2Seq, and SQLNet Models. 2024 9th International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering, 938-943. Antalya, Turkiye. https://doi.org/10.1109/UBMK63289.2024.10773579.
Shen, S., Logeswaran, L., Lee, M., Lee, H., Poria, S., & Mihalcea, R. (2024). Understanding the Capabilities and Limitations of Large Language Models for Cultural Commonsense. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2405.04655.
Sjödén, B. (2020). When Lying, Hiding and Deceiving Promotes Learning - A Case for Augmented Intelligence with Augmented Ethics. In Bittencourt, I. I., Cukurova, M., Muldner, K., Luckin, R., & Millán, E. (Eds), Artificial Intelligence in Education (12164, 291-295). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-52240-7_53.
Verhagen, T., Van Nes, J., Feldberg, F., & Van Dolen, W. (2014). Virtual Customer Service Agents: Using Social Presence and Personalization to Shape Online Service Encounters. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 19(3), 529-545. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcc4.12066.
Vogt, J. (2021). Where is the Human Got to Go? Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Big Data, Digitalisation, and Human-Robot Interaction in Industry 4.0 and 5.0. AI & Society, 36(3), 1083-1087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-020-01123-7.
Wagner, K., & Schramm-Klein, H. (2019, December 15-18). Alexa, Are You Human? Investigating Anthropomorphism of Digital Voice Assistants - A Qualitative Approach. International Conference on Information Systems 2019, 7. Munich, Germany.
Wangdi, P. (2024). Integrating Artificial Intelligence in Education: Trends and Opportunities. International Journal of Research in STEM Education, 6(2), 50-60. https://doi.org/10.33830/ijrse.v6i2.1722.
Waytz, A., Heafner, J., & Epley, N. (2014). The Mind in the Machine: Anthropomorphism Increases Trust in an Autonomous Vehicle. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 52, 113-117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2014.01.005.
Xue, Q. (2024). Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Exploration of Large Language Models in Natural Language Processing. Applied and Computational Engineering, 57(1), 247-252. https://doi.org/10.54254/2755-2721/57/20241341.
Yen, C., & Chiang, M. -C. (2021). Trust Me, If You Can: a Study on the Factors that Influence Consumers’ Purchase Intention Triggered by Chatbots Based on Brain Image Evidence and Self-Reported Assessments. Behaviour & Information Technology, 40(11), 1177-1194. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2020.1743362.
Yu, C. -E. (2020). Humanlike Robots as Employees in the Hotel Industry: Thematic Content Analysis of Online Reviews. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 29(1), 22-38. https://doi.org/10.1080/19368623.2019.1592733.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
หมวดหมู่
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2025 วารสารคอมพิวเตอร์และเทคโนโลยีสร้างสรรค์

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.






























